
In this case the balance sheet for the new partner’s business would serve as a basis for preparing the opening entry. The assets listed in the balance sheet are taken over, the liabilities partnership accounting are assumed, and the new partner’s capital account is credited for the difference. The Internal Revenue Service looks at corporations as independent taxable entities.. Accountants for corporations must understand where the company’s tax liabilities cut deepest and report these findings to upper management.
How Do the Owner’s Distributions Show in a Profit or Loss?
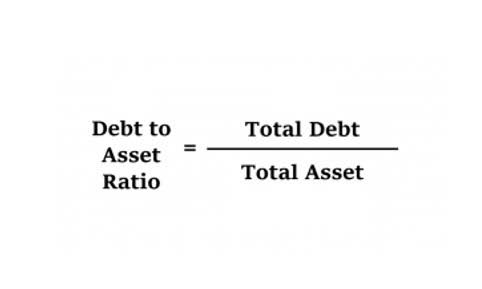
Partnership accounting begins with the foundational understanding of the partnership agreement, a legal document that outlines the terms and conditions under which the partnership operates. This agreement is not just a formality; it serves as the blueprint for all financial transactions and decisions within the partnership. It specifies how profits and losses are to be shared, the roles and responsibilities of each partner, and the procedures for admitting new partners or handling the withdrawal of existing ones. Without a well-drafted partnership agreement, the financial management of the partnership can become chaotic and contentious.
- This principle underscores the importance of trust and communication among partners, as the actions of one partner can bind the entire partnership.
- The double entry is completed with debit entries in the partners’ capital accounts.
- Assume that the three partners agreed to sell 20% of interest in the partnership to the new partner.
- Accounting helps a company track its cash flow and handle the payments it receives and makes.
- This document typically outlines the specific percentages or ratios by which profits and losses are to be divided among the partners.
- Each of the existing partners may agree to sell 20% of his equity to the new partner.
Key Financial Statements
- Assume that Partner A and Partner B admit Partner C as a new partner, when Partner A and Partner B have capital interests $30,000 and $20,000, respectively.
- The share that each partner gets is based on their old profit and loss sharing ratios.
- The balance sheet offers a snapshot of the partnership’s assets, liabilities, and equity at a specific point in time.
- This type of partnership is often chosen for its straightforward structure and ease of formation.
- Unlike corporate shareholders, partners have individual capital accounts that reflect their contributions, withdrawals, and share of profits or losses.
On the other hand, interest on drawings is a loss to the partner and debits to his Current/Capitals Account. Now, whenever you make a transaction, you have to ensure that the business is there on both ends. They are there to help you audit your transactions and ensure profits are passed between partners appropriately. Appropriations of profitAs there is no requirement for all of the appropriations considered below to be included by a specific partnership, exam questions may only include some of them. That means that you only need to deal with the appropriations referred to in the question. If the retiring partner’s interest is purchased by an outside party, the retiring partner’s equity is transferred to the capital account of the new partner, Partner D.
Investment of assets other than cash
- However, they must file a particular return with the IRS called Form 1065, which reports all income, gains, losses, deductions, and credits.
- The dynamics of a partnership can change significantly with the admission or withdrawal of partners, making these processes pivotal moments in the life of a business.
- Liquidation of a partnership generally means that the assets are sold, liabilities are paid, and the remaining cash or other assets are distributed to the partners.
- Proper management of capital accounts helps prevent disputes and provides a clear picture of each partner’s equity in the partnership.
Some partnership agreements refer to salaries or salary allowances for partners and interest on investments. These are not expenses of the business, they are part of the formula for splitting net income. Many partners use the components of the formula for splitting net income or loss to determine how much they will withdraw in cash from the business during the year, in anticipation of their share of net income. If the partnership uses the accrual basis of accounting, the partners pay federal income contra asset account taxes on their share of net income, regardless of how much cash they actually withdraw from the partnership during the year. Another point to remember is that the ‘appropriation account’ is an additional accounting statement that is required for a partnership.

This account is prepared to https://www.facebook.com/BooksTimeInc distribute profit or loss among the partners. This account show what amount of profit is transferred to partner’s capital Account. Goodwill, at its simplest, is the difference between the fair or market value of the net assets of the partnership and their book value.
- Appropriations of profitAs there is no requirement for all of the appropriations considered below to be included by a specific partnership, exam questions may only include some of them.
- Two or more individualsA partnership includes at least two individuals (partners).
- This is typically an amount of cash equal to each partner’s share of ownership in the business.
- This ensures that all partners are clear about their financial entitlements and responsibilities, fostering a transparent and cohesive business environment.
- If non-cash assets are sold for more than their book value, a gain on the sale is recognized.
- As can be seen, once the salary and interest portions are determined, they are added together to determine the amount of the remainder to be allocated.
- The capital account will be reduced by the amount of drawing made by the partner during the accounting period.
